Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe
Fe O
O
Gomez-Perez, J. M.*; Oyanagi, Koichi*; Yahiro, Reimei*; Ramos, R.*; Hueso, L. E.*; Saito, Eiji; Casanova, F.*
Applied Physics Letters, 116(3), p.032401_1 - 032401_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.43(Physics, Applied) C based on two binary non-ideal solid solutions
C based on two binary non-ideal solid solutionsWalker, C.; Suto, Shunkichi; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Cement and Concrete Research, 79, p.1 - 30, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:69 Percentile:90.65(Construction & Building Technology)Modeling the solubility behavior of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel is important to make quantitative predictions of the degradation of hydrated ordinary Portland cement (OPC) based materials. Experimental C-S-H gel solubility data have been compiled from the literature, critically evaluated and supplemented with new data from the current study for molar Ca/Si ratios = 0.2-0.83. All these data have been used to derive a discrete solid phase (DSP) type C-S-H gel solubility model based on two binary non-ideal solid solutions in aqueous solution(SSAS). Features of the DSP type C-S-H gel solubility model include satisfactory predictions of pH values and Ca and Si concentrations for all molar Ca/Si ratios = 2.7  0 in the C-S-H system, portlandite (CH) for Ca/Si ratios
0 in the C-S-H system, portlandite (CH) for Ca/Si ratios  1.65, congruent dissolution at Ca/Si ratios = 0.85, and amorphous silica (SiO
1.65, congruent dissolution at Ca/Si ratios = 0.85, and amorphous silica (SiO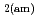 ) for Ca/Si ratios
) for Ca/Si ratios  0.55 as identified in the current study by IR spectroscopy.
0.55 as identified in the current study by IR spectroscopy.
Sato, Shinichiro; Beernink, K.*; Oshima, Takeshi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 54(6), p.061401_1 - 061401_6, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.94(Physics, Applied)Performance degradation and immediate recovery of a-Si/a-SiGe/a-SiGe triple-junction solar cells due to irradiation of silicon ions, electrons, and protons are investigated. Significant recovery is always observed independent of radiation species and temperature. It is shown that the characteristic time, which is obtained by analyzing the short-circuit current annealing behavior, is an important parameter for practical applications in space. In addition, the radiation degradation mechanism is discussed by analyzing the energy loss process of incident particles (ionizing energy loss: IEL, and non-ionizing energy loss: NIEL) and their relative damage factors. It is determined that ionizing dose is the primarily parameter for electron degradation whereas displacement damage dose is the primarily parameter for proton degradation. The impact of "radiation quality effect" has to be considered to understand the degradation due to Si ion irradiation.
Sugimoto, Masaki
Kogyo Zairyo, 53(12), p.75 - 79, 2005/12
no abstracts in English
Agui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Asahi, Toru*
Hoshako, 18(4), p.215 - 222, 2005/07
no abstracts in English
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.792, p.379 - 384, 2004/00
We have studied high-energy ion irradiation effects in bismuth by measuring the electrical resistivity at low temperature in relation to its structural change. Bismuth thin films (300-600  10 K with several kinds of energetic (100-200 MeV) heavy ions. The resistivity of the specimen is measured in-situ at
10 K with several kinds of energetic (100-200 MeV) heavy ions. The resistivity of the specimen is measured in-situ at  7 K during irradiation. After irradiation, annealing behavior of the resistivity is observed up to
7 K during irradiation. After irradiation, annealing behavior of the resistivity is observed up to  35 K. The temperature dependence of the resistivity during annealing shows an abrupt increase around 20 K, implying re-crystallization of irradiation-induced amorphous region. Since amorphous bismuth also shows a superconducting transition below
35 K. The temperature dependence of the resistivity during annealing shows an abrupt increase around 20 K, implying re-crystallization of irradiation-induced amorphous region. Since amorphous bismuth also shows a superconducting transition below  6 K, high-density electronic excitation due to energetic heavy-ion irradiation may induce columnar region of superconducting amorphous bismuth in normal crystalline bismuth. We are trying to detect the superconducting transition as a result of irradiation-induced amorphization.
6 K, high-density electronic excitation due to energetic heavy-ion irradiation may induce columnar region of superconducting amorphous bismuth in normal crystalline bismuth. We are trying to detect the superconducting transition as a result of irradiation-induced amorphization.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Mizuki, Junichiro; Katayama, Ryoko*; Yagi, Kenichiro*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Hamazaki, Shinichi*; Takashige, Masaaki*
Applied Physics Letters, 83(2), p.275 - 277, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:57.36(Physics, Applied)We observed an intermediate structure during the re-crystallization process from the amorphous state of Bi Ti
Ti O
O prepared by rapid quenching. The intermediate structure which appears during the re-crystallization process consists of two phases; one is pyrochlore Bi
prepared by rapid quenching. The intermediate structure which appears during the re-crystallization process consists of two phases; one is pyrochlore Bi Ti
Ti O
O phase and the other is a stacking-fault induced structure under the excessive Bi condition. The microstructure of the stacking-fault induced structure was investigated by synchrotron X-ray diffraction. In the case of a large number of Bi
phase and the other is a stacking-fault induced structure under the excessive Bi condition. The microstructure of the stacking-fault induced structure was investigated by synchrotron X-ray diffraction. In the case of a large number of Bi O
O , some are inserted between the pseudo-perovskite layers of Bi
, some are inserted between the pseudo-perovskite layers of Bi Ti
Ti O
O , and a non-stoichiometric Bi
, and a non-stoichiometric Bi WO
WO -like structure is stabilized.
-like structure is stabilized.
 -implanted 6H-SiC studied by monoenergetic positron beams
-implanted 6H-SiC studied by monoenergetic positron beamsUedono, Akira*; Tanigawa, Shoichiro*; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Nashiyama, Isamu; Frank, T.*; Pensl, G.*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*; Odaira, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 87(9), p.4119 - 4125, 2000/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:49.32(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Dai; Morimoto, Iwao; Zheng, X.; Maebara, Sunao; Nakajima, Mitsuo*; Horioka, Kazuhiko*; Kono, Toshiyuki*; Shiho, Makoto
JAERI-Research 2000-018, p.66 - 0, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Kakuta, Tsunemi; Sakasai, Kaoru; *; *;
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 258-263, p.1893 - 1896, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:81.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Koizumi, Satoshi
Journal of Chemical Physics, 107(2), p.603 - 612, 1997/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.6(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sakasai, Kaoru; Ara, Katsuyuki; Ito, Hirokuni; Kishimoto, Maki; Katagiri, Masaki
Review of Scientific Instruments, 65(5), p.1657 - 1662, 1994/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.93(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Sakasai, Kaoru; Ara, Katsuyuki; Ito, Hirokuni; Kishimoto, Maki; Katagiri, Masaki; *
MAG-93-9, p.71 - 76, 1993/01
no abstracts in English
 Pb
Pb Sr
Sr Ca
Ca Cu
Cu O
O ceramic
ceramic*; *; *; *
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 31(8A), p.L1037 - L1040, 1992/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:32.82(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Kushita, Kohei; Hojo, Kiichi; Furuno, Shigemi;
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 191-194, p.346 - 350, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
 Pb
Pb Sr
Sr Ca
Ca Cu
Cu O
O superconductor
superconductorShiraishi, Kensuke; *; *
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 30(7B), p.L1260 - L1263, 1991/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:65.26(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 phase in Pb-free Bi-Sr-Ca-Cu-O thin film
phase in Pb-free Bi-Sr-Ca-Cu-O thin film*; *; *; Shiraishi, Kensuke
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 30(5A), p.L826 - L829, 1991/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.21(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
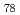 B
B Si
Si alloy
alloyKatano, Susumu; Morii, Yukio; Iizumi, Masashi; H.R.Child*; R.M.Nicklow*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 56(9), p.3196 - 3200, 1987/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:36.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Shinku, 27(7), p.589 - 595, 1984/00
no abstracts in English
Okumura, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Machine-learning molecular dynamics (MLMD) is an atomistic-scale simulation method that has achieved high accuracy and low computational cost, attracting attention in the nuclear energy research field. However, it has yet to be available to everyone. We are developing an integrated MLMD system that enables anyone to perform MLMD simulations. In this presentation, the presenter will give an overview of the system, its development progress, and how to use it in practice. Furthermore, the MLMD simulation of amorphous ice, a difficult material to handle in simulations because it is an amorphous state of polar molecules, will be shown as an example.
Okumura, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Recently, the chemical process of organic matter formation by chemical reactions on the surface of amorphous ice, which constitutes the interstellar dust surface, has attracted much attention. In addition to experiments, simulation of this phenomenon is useful, but no simulation study has yet evaluated the effects of amorphous ice on the surface of interstellar dust. Therefore, we aim to simulate this chemical process using machine-learning molecular dynamics, which can accurately simulate both chemical reactions and amorphous materials. In this presentation, we will report the results of the simulation of ice and water by machine learning molecular dynamics, including technical aspects, and discuss future prospects.